Technical Analysis
Learn how to use historical data and chart, to get market overview and elevate your trading strategies.
Technical analysis has to do with forecasting future financial price movements based on past price movements.
Moving Average
How does Moving Average work?
Moving Average on the chart
Determine price trends
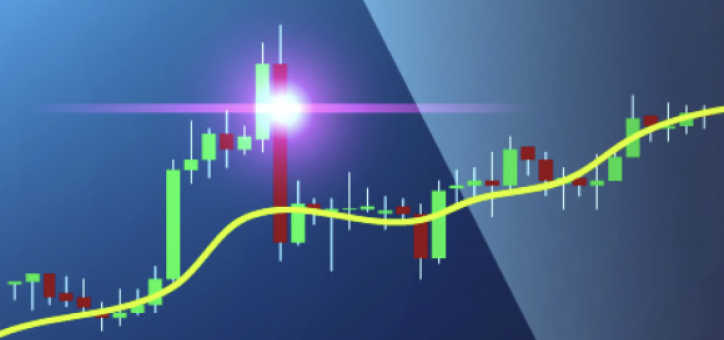
As shown in the USD/JPY Price Chart below, price is below the 200-day moving average at the beginning and creates an downward trend.
When the USD/JPY price approached the 200-day moving average, there is a possibility of a turning trend. In below chart, upward trend started after the price hit the 200-day moving average.
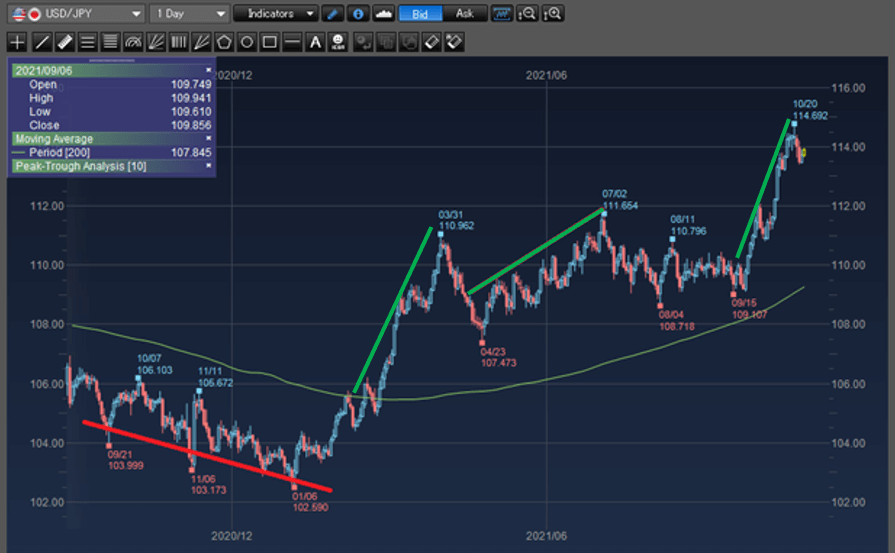
Determine entry signals (Golden Cross, Death Cross)
Crossing of two moving averages with different timeline is commonly used to find buy and sell entry signals.
Golden Cross
When the shorter period average (the fast lane) rises over the longer period average (the slow lane), the recent trend is breaking the long-term trend and creates the buy signal.
Death Cross
When the shorter period(the fast lane) drops below the longer period (the slow lane), the recent trend is breaking the long-term trend and creates the sell signal.
Below is an example of Gold Cross and Death Cross using 20-day moving average (red line) as the fast line, and a 50-day average (blue line) as the slow line in the price chart.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
How does RSI work?
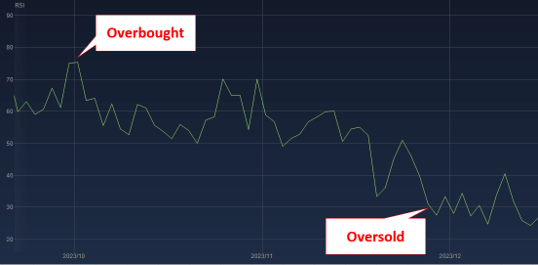
RSI on the chart
Bollinger Bands
How does Bollinger Bands work?
B. A middle band is the average price over a specific period.
C. A lower band is the middle band minus two standard deviations.
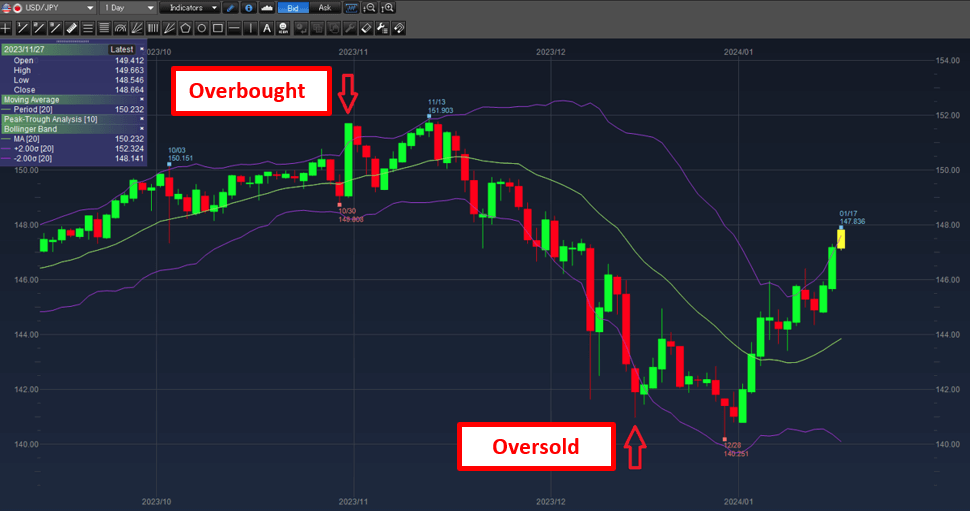
Bollinger bands on the chart
When price action is close to the upper band, the current price of the asset is considered high relative to recent prices, when price touches or breaks above the upper band, traders consider it to be overbought.
When price moves close to the lower band, the current price is considered low relative to recent prices. When the price of the asset touches or breaks below the lower band of the Bollinger Bands, traders consider it to be oversold.
Fibonacci Retracement
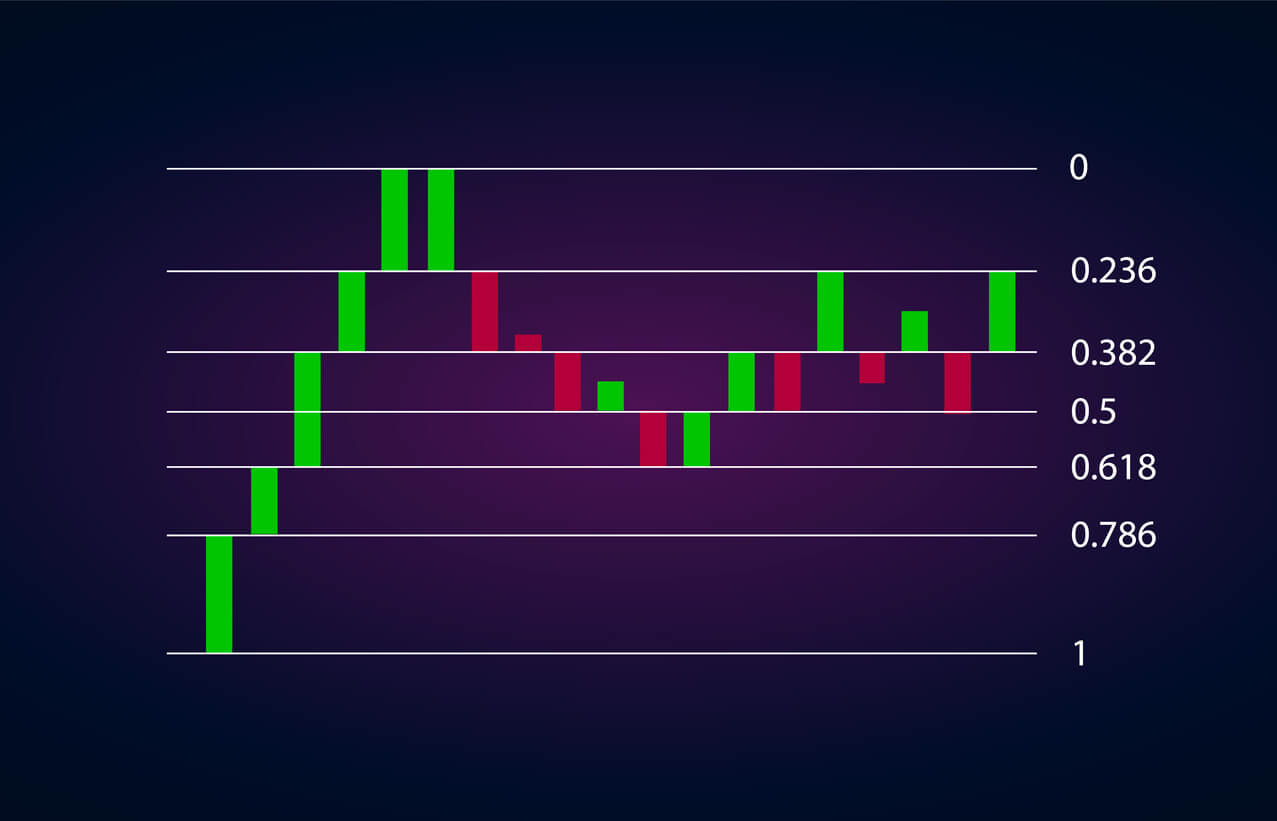
How does Fibonacci Retracement work?
Fibonacci Retracement on the chart
Identify a trend
For example, in the EUR/JPY daily chart below, there was an uptrend from 146.128 to 164.296. The price then started to go down.
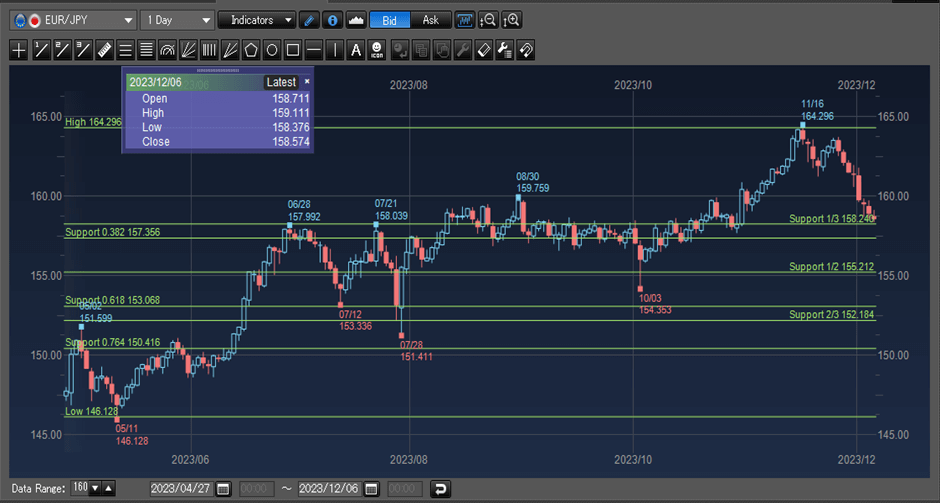
Decide which level is a good support and take-profit when target price reached
Assume traders believed EUR/JPY would go up again after some rebound, to decide where to place a buy order, traders could use Fibonacci retracement as the reference support levels. In this case the price went down to around 61.8% retracement level (153.068) of the identified trend and goes up again. If traders think the price would at least go back to 38.2% resistance level, a take-profit order could be placed at around 157.356.
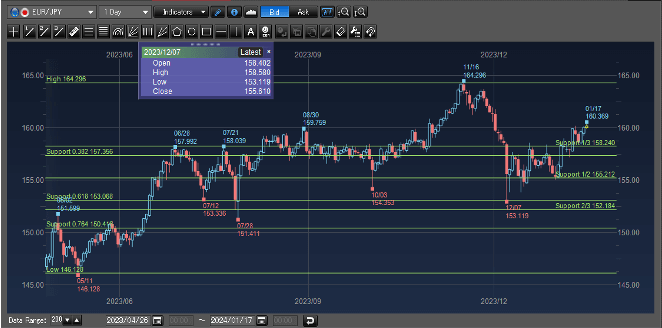
Stop-loss when things are not going right
On the other hand, to better control risk, traders are advised to prepare for potential trend direction change. In this case a stop-loss order could be placed below the 61.8% support level to close the existing buy EUR/JPY position to limit your loss in case EUR/JPY price went down further.