What is Forex?
What Is Forex
Forex, short for the foreign exchange, is the global marketplace where currencies are traded. It's the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, and operates 24 hours a day.
Forex traders exchange two different currencies and make profits from the price difference in buy and sell price.
As the value of currencies keep changing, traders can earn profits by trading at the right timing.

Example
When the US dollar is expected to weaken in value relative to the euro, forex traders would sell dollars to buy euros.
If the euro actually appreciates, traders would sell euros and buy back more dollars than they originally had, making a profit.
Currency Pairs
Currency Pairs
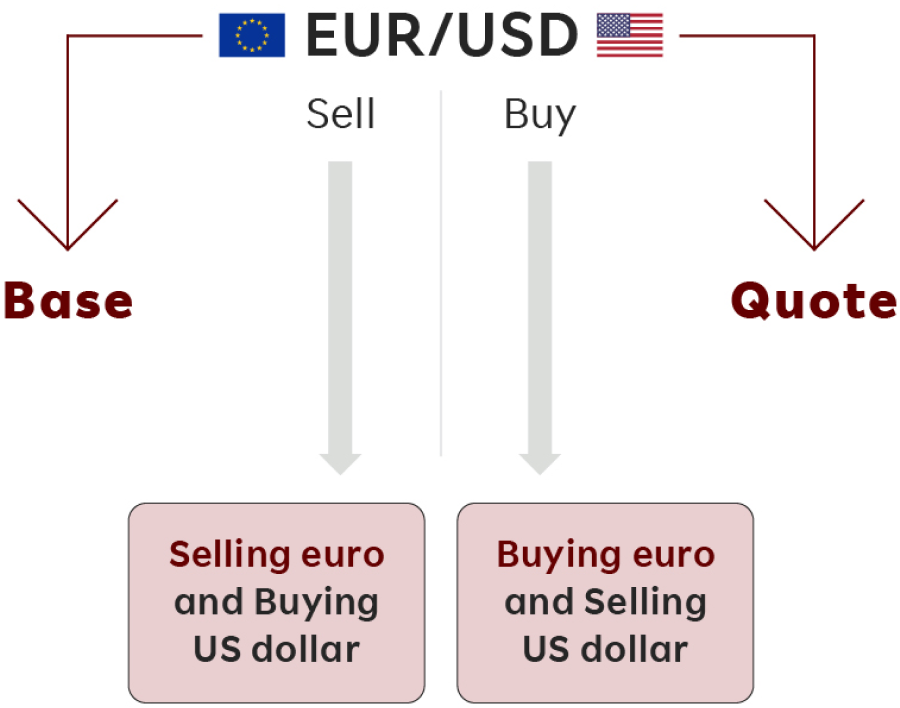
Currencies are quoted in pairs, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY. The first listed currency is known as the base currency, while the second is called the counter or quote currency. The base currency is the “basis” for the buy or the sell.
Exchange Rate
The exchange rate is the price of the one currency in terms of another currency.
It tells you how much of one currency traders need to spend to purchase one unit of another currency.
Example
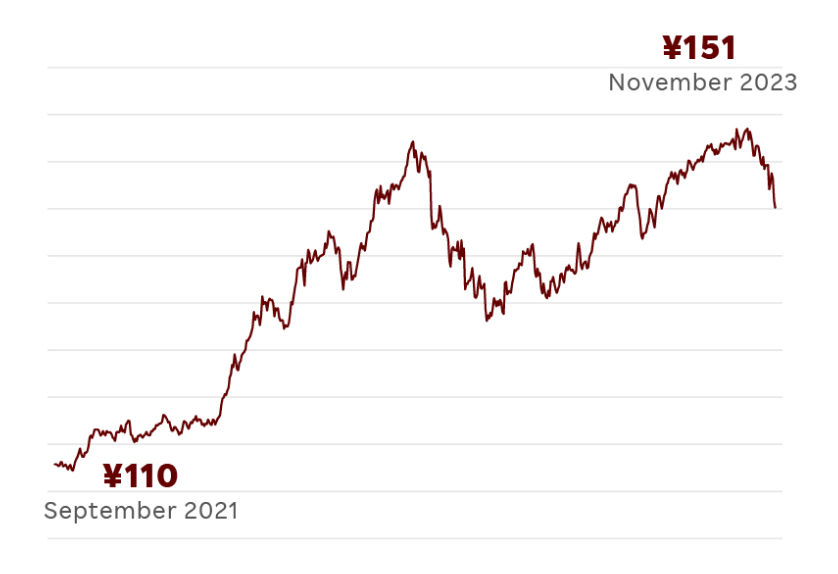
USD/JPY Exchange Rate
USD/JPY Exchange Rate
In September 2021, one US dollar was worth about 110 Japanese yen. By November 2023, it increased to about 151 yen. The US dollar increased in value by about 27.2% relative to the yen during this time.
Trade size (lot)
A lot is the smallest trade size available. Rakuten Securities HK accounts have a lot size of 1K (1,000) units of currency. Account holders can however place trades of different sizes, so long as they are in increments of 1K units.
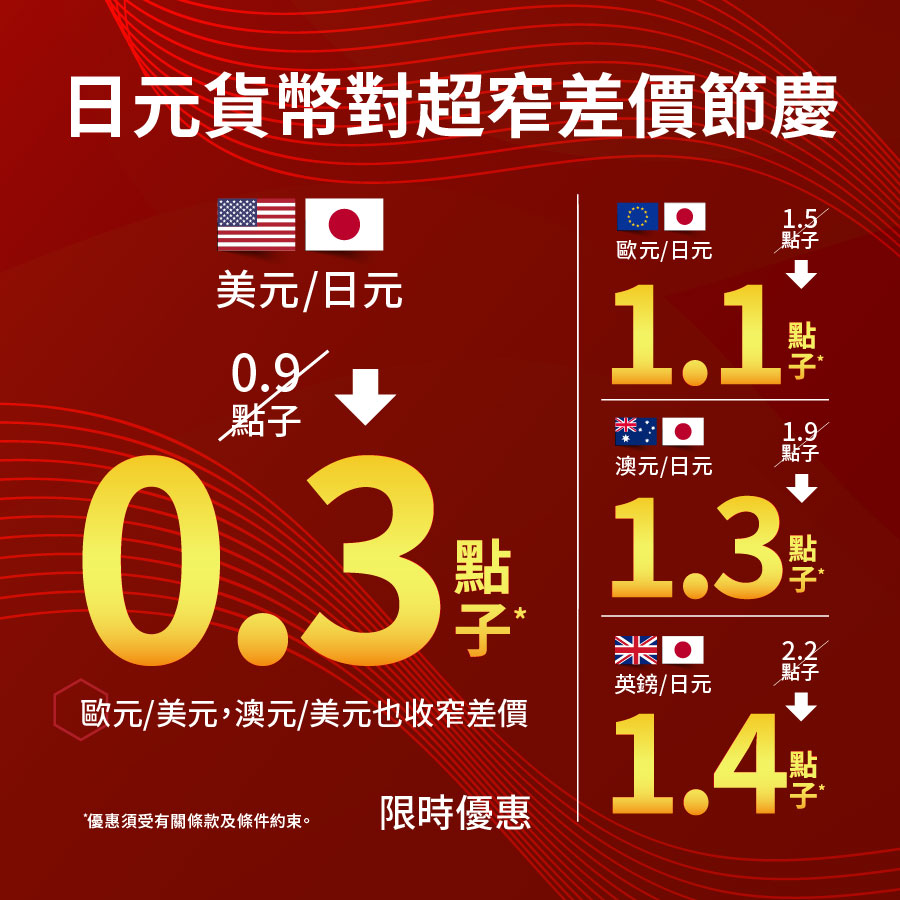
Spreads
There are buy and sell prices for every currency pair and the difference between the price is called the spread. For example, if USD/JPY pair's Sell price is 142.124 and Buy price is 142.129, the spread is 0.5 pips.

Pip
A pip (percentage in point) is a unit of movement in the exchange rate.
For most of currency pairs, The fourth decimal places is counted as "pips" , and one pip is 0.0001.
For Japanese Yen-related currency pairs, the secound decimal places is counted as "pips", and one pip is 0.01.
Example
EUR/USD rises from 1.16997 to 1.17007, the EUR/USD has risen 1 pip.
USD/JPY drops from 110.200 to 110.145, the USD/JPY has dropped 5.5 pip.
USD/JPY drops from 110.200 to 110.145, the USD/JPY has dropped 5.5 pip.
Leverage
Forex allows traders to trade a large amout with a relatively small fund.
As we offer leverage of 20:1, traders can trade with $1,000 in the market by setting aside only $50 as a margin.
As we offer leverage of 20:1, traders can trade with $1,000 in the market by setting aside only $50 as a margin.
Margin
Margin is the amount of fund that traders need to trade and hold a leveraged position.
The required margin level at Rakuten Securities Hong Kong is as follows.
Initial Margin:
Margin level must exceed 5% of open positions value in order to open a new position.
Margin level must exceed 5% of open positions value in order to open a new position.
Maintenance Margin:
Margin level must exceed 3% of open positions value to keep positions.
Margin level must exceed 3% of open positions value to keep positions.
Liquidation:
Positions will be automatically closed when margin level falls below 2% of open positions.
Positions will be automatically closed when margin level falls below 2% of open positions.
Rollover
Rollover, also known as swap, is the interest earned or paid for a position kept open overnight, which is caused by a interest rate differential between the currency pair traded.
Exclusive education & support


Market insights
Keep up with the forex market, take advantage of each investment opportunity.

Extensive 1-on-1 support
Get in touch with our Professional Support Team by phone, email or WhatsApp for immediate support.